
Meta Description:
Learn what high bilirubin in the blood means, its causes, symptoms, and the most effective medical treatments and lifestyle strategies to control and reduce elevated bilirubin levels safely.
1. Treatment for High Bilirubin in the Blood: Causes, Medical Care, and How to Control It
High bilirubin levels in the blood, a condition known as hyperbilirubinemia, can be a sign that something is not functioning properly in the body—most often the liver, gallbladder, or red blood cells. While mild elevations may be harmless, persistently high bilirubin can indicate serious underlying health issues that require medical attention.
This comprehensive guide explains what bilirubin is, why it becomes elevated, the available medical treatments, and practical ways to control and manage high bilirubin through lifestyle and dietary measures.
Treatment for High Bilirubin in the Blood: Causes, Medical Care, and How to Control It…
2. What Is Bilirubin?
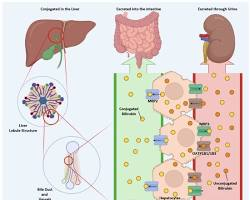
Bilirubin is a yellowish substance produced when red blood cells break down naturally at the end of their lifespan (about 120 days). This process occurs in the spleen and bone marrow. The bilirubin then travels to the liver, where it is processed and excreted through bile into the digestive tract, eventually leaving the body in stool.
There are two main types of bilirubin:
- Unconjugated (indirect) bilirubin: Not yet processed by the liver
- Conjugated (direct) bilirubin: Processed by the liver and ready for excretion
A blood test measuring total, direct, and indirect bilirubin helps doctors determine the cause of elevated levels.
Treatment for High Bilirubin in the Blood: Causes, Medical Care, and How to Control It…
3. What Causes High Bilirubin Levels?
High bilirubin can occur when any step in its production, processing, or elimination is disrupted. Common causes include:
1. Liver Diseases
- Hepatitis (viral, alcoholic, or autoimmune)
- Cirrhosis
- Fatty liver disease
- Liver cancer
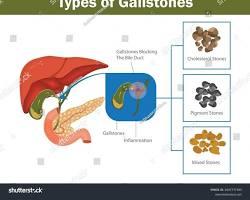
2. Gallbladder and Bile Duct Problems
- Gallstones
- Bile duct obstruction
- Cholestasis (reduced bile flow)
3. Blood Disorders
- Hemolytic anemia
- Sickle cell disease
- Thalassemia
4. Genetic Conditions
- Gilbert syndrome (usually mild and benign)
- Crigler-Najjar syndrome (rare but severe)
5. Medications and Toxins
- Certain antibiotics
- Acetaminophen overdose
- Chemotherapy drugs
- Excessive alcohol use
4. Symptoms of High Bilirubin
Symptoms vary depending on the cause and severity but may include:
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice)
- Dark-colored urine
- Pale or clay-colored stools
- Fatigue and weakness
- Abdominal pain or swelling
- Nausea and vomiting
- Itching (especially in liver-related causes)
In newborns, high bilirubin is common and usually temporary, but in adults it often signals an underlying issue.
5. Medical Treatment for High Bilirubin in the Blood
Treatment for high bilirubin focuses on addressing the underlying cause, not just lowering the bilirubin number itself.
1. Treating Liver Conditions
- Antiviral medications for viral hepatitis
- Steroids or immunosuppressants for autoimmune hepatitis
- Lifestyle changes and medications for fatty liver disease
- Liver transplantation in advanced liver failure
2. Managing Gallbladder and Bile Duct Issues
- Gallstone removal (surgery or endoscopic procedures)
- Bile duct stenting to relieve obstruction
- Antibiotics if infection is present
3. Treating Blood Disorders
- Medications or blood transfusions for hemolytic anemia
- Treatment of underlying genetic conditions
- Folic acid supplementation in some cases
4. Newborn Treatment (Brief Note)
In infants, treatment may include:
- Phototherapy (light therapy)
- Exchange transfusion in severe cases
5. Medication Review
If high bilirubin is drug-induced, doctors may:
- Adjust dosage
- Discontinue the offending medication
- Switch to safer alternatives
6. How to Control and Reduce High Bilirubin Naturally
While medical treatment is essential, lifestyle and dietary measures play a major role in supporting liver health and controlling bilirubin levels.
1. Support Liver Health Through Diet
A liver-friendly diet can significantly help control bilirubin levels.
Recommended foods:
- Leafy greens (spinach, kale)
- Cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, cauliflower)
- Fresh fruits (berries, citrus fruits)
- Whole grains (oats, brown rice)
- Lean proteins (fish, chicken, legumes)
- Healthy fats (olive oil, nuts)
Foods to limit or avoid:
- Alcohol (one of the most critical factors)
- Fried and processed foods
- Sugary drinks and desserts
- Excessive red meat
- High-sodium foods
2. Stay Well Hydrated
Adequate water intake helps the liver and kidneys flush toxins and supports proper bile flow. Aim for 6–8 glasses of water daily unless otherwise advised by a doctor.
3. Avoid Alcohol Completely
Alcohol is processed by the liver and can significantly worsen bilirubin levels. Even moderate drinking can be harmful if bilirubin is elevated. In many cases, complete abstinence is necessary to allow the liver to heal.
4. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Obesity is closely linked to fatty liver disease, a common cause of high bilirubin. Gradual weight loss through a balanced diet and regular physical activity can improve liver function and reduce bilirubin over time.
5. Exercise Regularly (Moderately)
Physical activity improves metabolism and liver efficiency. Recommended options include:
- Brisk walking
- Swimming
- Cycling
- Yoga
Avoid extreme or intense exercise if you have advanced liver disease, as it may increase stress on the body.
6. Be Careful With Medications and Supplements
Many over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements are processed by the liver. Avoid:
- Unnecessary painkillers
- Herbal remedies without medical approval
- High-dose vitamin supplements
Always consult a healthcare provider before starting or stopping any medication.
7. Manage Stress and Sleep Well
Chronic stress and poor sleep can negatively affect liver health and immune function. Aim for:
- 7–9 hours of sleep per night
- Stress-reducing activities like meditation or breathing exercises
7. When to See a Doctor
Seek medical attention if you experience:
- Persistent jaundice
- Severe abdominal pain
- Confusion or drowsiness
- Sudden swelling in the abdomen or legs
- Rapid worsening of symptoms
High bilirubin should never be ignored, especially in adults, as early diagnosis can prevent serious complications.
8. Can High Bilirubin Be Prevented?
Not all causes are preventable, but you can lower your risk by:
- Avoiding excessive alcohol
- Getting vaccinated for hepatitis A and B
- Practicing safe sex and avoiding needle sharing
- Maintaining a healthy diet and weight
- Getting regular health checkups
Final Thoughts
High bilirubin in the blood is not a disease itself but a sign of an underlying problem—most often related to the liver, gallbladder, or blood. Effective treatment depends on identifying and addressing the root cause. Medical therapies, combined with lifestyle and dietary changes, can significantly reduce bilirubin levels and improve overall health.
If you have elevated bilirubin on a blood test, work closely with a healthcare professional to determine the cause and develop a personalized treatment plan. With proper care and healthy habits, many people successfully control high bilirubin and protect their long-term liver health.




