Hydrocephalus affects the brain by causing fluid buildup. This condition can impact life expectancy.
Hydrocephalus, often called “water on the brain,” can occur at any age. The condition involves an abnormal buildup of cerebrospinal fluid within the brain’s ventricles. This fluid buildup can increase pressure on the brain, leading to various symptoms. Treatment options, such as shunts or endoscopic procedures, can help manage the condition.
But many wonder about the long-term outlook. Life expectancy with hydrocephalus can vary based on several factors. Early diagnosis and effective treatment play crucial roles. Understanding these factors can help manage expectations and improve quality of life. Let’s explore what influences the life expectancy of someone with hydrocephalus.
What Is Hydrocephalus
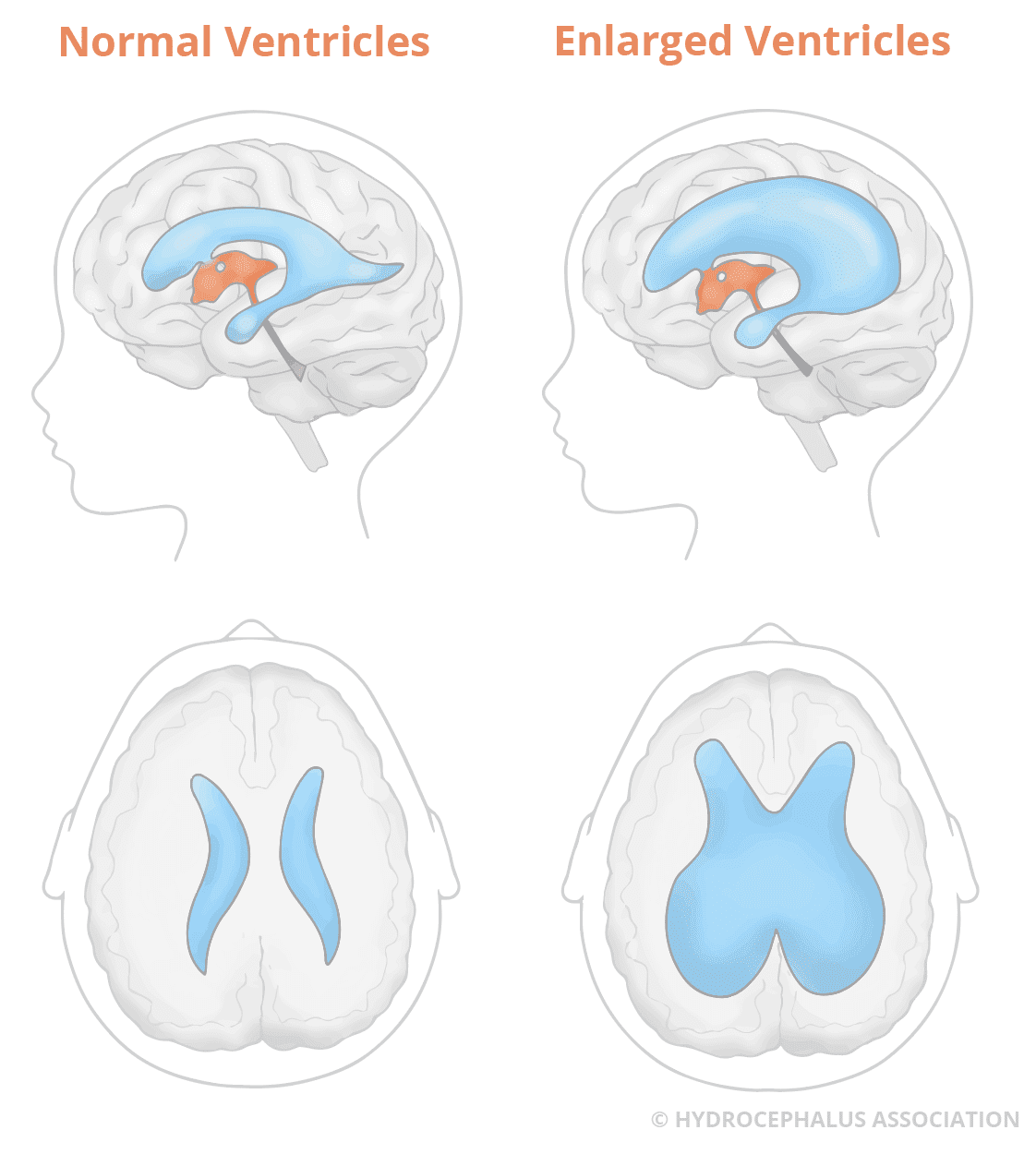
Hydrocephalus is a medical condition that affects the brain. It involves an abnormal buildup of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the brain’s ventricles. This can lead to increased pressure on the brain and can cause various symptoms and complications. Understanding hydrocephalus and its impact on life expectancy is important for those affected and their families.
Definition And Types
Hydrocephalus comes from Greek words meaning “water on the brain.” It can be present at birth or develop later. There are two main types of hydrocephalus:
- Congenital hydrocephalus: This type is present at birth. It can result from genetic abnormalities or issues during fetal development.
- Acquired hydrocephalus: This type develops after birth. It can be caused by infections, tumors, or head injuries.
Common Symptoms
Hydrocephalus symptoms vary with age and the condition’s severity. Common symptoms in infants include:
- An unusually large head
- Rapid head growth
- Vomiting
- Sleepiness
In older children and adults, symptoms can include:
- Headaches
- Nausea
- Vision problems
- Balance difficulties
Recognizing these symptoms early can help in seeking timely medical intervention.

Credit: www.hydroassoc.org
Causes Of Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus, often referred to as “water on the brain,” is a condition characterized by an excess of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the brain’s ventricles. Understanding the causes of hydrocephalus is crucial for diagnosing and managing the condition. There are two main categories that explain why this condition might occur: congenital factors and acquired factors. Let’s delve deeper into each.
Congenital Factors
Congenital hydrocephalus is present at birth and can result from a variety of genetic and environmental influences. One common cause is aqueductal stenosis, where the narrow passage between the third and fourth ventricles is blocked. This blockage prevents CSF from flowing properly, leading to fluid buildup.
Another cause can be neural tube defects, such as spina bifida, where the spinal cord doesn’t form correctly. This condition can interfere with normal CSF circulation. Additionally, genetic abnormalities and infections during pregnancy, like rubella or toxoplasmosis, can also contribute to the development of hydrocephalus.
Acquired Factors
Unlike congenital hydrocephalus, acquired hydrocephalus develops after birth due to various factors. One major culprit is head injury. Traumatic brain injuries can disrupt the normal flow of CSF, causing it to accumulate.
Another significant factor is infections such as meningitis, which inflame the brain’s tissues and can obstruct CSF pathways. Similarly, tumors in the brain can block CSF flow, leading to hydrocephalus.
Moreover, hemorrhages, particularly in premature babies, can cause blood to mix with CSF, resulting in clogged pathways and fluid accumulation. Finally, normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH), often seen in older adults, is a condition where CSF builds up without a clear reason, leading to symptoms like walking difficulties, dementia, and urinary incontinence.
Understanding these causes helps in diagnosing hydrocephalus early and managing it effectively. Whether congenital or acquired, recognizing the underlying factors is the first step towards better health outcomes for those affected by this condition.
Diagnosis Of Hydrocephalus
Diagnosing hydrocephalus early is crucial for effective treatment. It involves several steps and techniques. Understanding these can help you stay informed about the process.
Medical History And Physical Exam
The first step in diagnosing hydrocephalus is taking a detailed medical history. This includes past health issues and family medical history. The doctor will ask about symptoms like headaches, nausea, or balance problems.
A physical exam follows. The doctor checks for signs of increased pressure in the brain. This may include looking at reflexes, muscle strength, and coordination. Sometimes, the doctor may look at the eyes for signs of pressure.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests are essential for diagnosing hydrocephalus. Common tests include MRI and CT scans. These tests provide detailed images of the brain.
An MRI uses magnetic fields to create detailed brain images. It helps detect fluid build-up and any structural abnormalities.
A CT scan uses X-rays to create cross-sectional brain images. It can quickly show fluid accumulation and brain structure.
These imaging tests help doctors confirm the diagnosis and plan treatment. They are non-invasive and provide crucial information.
Treatment Options
Living with hydrocephalus can be challenging, but the good news is that there are effective treatment options available. These treatments can help manage the condition and improve the quality of life for individuals affected by hydrocephalus. In this section, we will explore two main treatment options: shunt systems and endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV). Understanding these options can help you make informed decisions about managing hydrocephalus.
Shunt Systems
Shunt systems are the most common treatment for hydrocephalus. A shunt is a flexible tube that is surgically placed in the brain to divert excess cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to another part of the body, where it can be absorbed. This helps relieve pressure on the brain. There are different types of shunt systems, including:
- Ventriculoperitoneal (VP) Shunt: This type diverts CSF from the brain to the abdominal cavity.
- Ventriculoatrial (VA) Shunt: This type diverts CSF from the brain to the heart.
- Ventriculopleural (VPL) Shunt: This type diverts CSF from the brain to the pleural space in the lungs.
Shunt systems can be very effective, but they do come with some risks. For example, shunts can become blocked or infected, and they may need to be replaced over time. Regular follow-up with a healthcare provider is crucial to ensure the shunt is working properly.
Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy
Endoscopic third ventriculostomy, or ETV, is another treatment option for hydrocephalus. This procedure involves making a small hole in the floor of the third ventricle in the brain, allowing CSF to bypass the blockage and flow more freely. ETV can be a good alternative to shunt systems for some patients, especially those with certain types of obstructive hydrocephalus.
ETV has several benefits:
- No Foreign Object: Unlike shunt systems, ETV does not involve implanting a foreign object in the body.
- Lower Risk of Infection: Since there is no shunt, the risk of infection is generally lower.
- Fewer Complications: ETV may have fewer long-term complications compared to shunts.
However, ETV is not suitable for everyone. The success of the procedure can depend on factors like the patient’s age and the specific cause of the hydrocephalus. It is important to discuss with your doctor whether ETV is a viable option for you.
Both shunt systems and ETV offer hope for those living with hydrocephalus. Deciding on the best treatment involves careful consideration of your individual circumstances and close consultation with your healthcare team. Remember, you are not alone in this journey. With the right treatment, many people with hydrocephalus lead full, active lives.
Factors Affecting Life Expectancy
When it comes to understanding life expectancy with hydrocephalus, several factors come into play. The age at diagnosis and the severity of the condition are crucial aspects that can significantly influence outcomes. In this section, we’ll delve into these factors, breaking down what they mean and how they impact individuals living with hydrocephalus.
Age At Diagnosis
Age plays a significant role in determining life expectancy for those with hydrocephalus. Diagnosing hydrocephalus at an early age can often lead to better management and improved outcomes. For instance:
- Infants and Young Children: Early diagnosis in infants allows for timely intervention, which can prevent complications and promote normal development. Doctors usually recommend a shunt surgery or an endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV) to drain excess fluid, which can help manage symptoms effectively.
- Adults: Hydrocephalus diagnosed in adulthood can be more complex. Symptoms might have been present for a long time, leading to other health issues. However, with proper treatment, many adults can lead a relatively normal life.
Severity Of Condition
The severity of hydrocephalus can vary widely among individuals. This variability impacts life expectancy. Here are some key points to consider:
- Congenital Hydrocephalus: This form is present at birth and can range from mild to severe. The extent of brain damage and associated disabilities can influence overall prognosis. Early and consistent medical care is crucial in managing the condition.
- Acquired Hydrocephalus: This type develops after birth due to infections, injuries, or other medical conditions. The severity depends on the underlying cause and how quickly it is addressed. Prompt treatment can mitigate further complications.
| Severity | Impact on Life Expectancy |
|---|---|
| Mild | With appropriate treatment, individuals can enjoy a near-normal life span. |
| Moderate | May require ongoing medical care and regular monitoring, but many lead fulfilling lives. |
| Severe | Higher risk of complications, necessitating comprehensive and continuous medical attention. |
In summary, the age at diagnosis and the severity of the condition are pivotal in determining life expectancy for those with hydrocephalus. Early diagnosis and effective management can significantly improve outcomes, allowing many to lead productive lives. If you or a loved one is dealing with hydrocephalus, understanding these factors can help in navigating the journey with informed decisions and a proactive approach.
Living With Hydrocephalus
Living with hydrocephalus presents unique challenges. Many people manage it well with the right support. Daily routines can make a big difference. Understanding and support from family, friends, and healthcare providers is crucial.
Daily Management
Daily management involves regular medical check-ups. Monitoring symptoms is important. Small changes can indicate issues. Staying hydrated is crucial. Proper diet and exercise help maintain overall health. Medication may be prescribed. It’s important to follow the treatment plan.
Support Systems
Support systems are vital for those with hydrocephalus. Family and friends play a key role. They provide emotional support. They assist with daily tasks. Support groups offer a sense of community. Sharing experiences helps. Healthcare providers offer medical guidance. They adjust treatments as needed. Mental health professionals help manage anxiety and stress. They provide coping strategies.
Prognosis And Long-term Outlook
Hydrocephalus is a condition where excess fluid builds up in the brain. This can impact life expectancy, but treatment options have improved over time. With proper care, many individuals live long, fulfilling lives. The long-term outlook varies based on several factors.
Quality Of Life
Quality of life for those with hydrocephalus can be high. Early diagnosis and effective treatment are crucial. Many lead normal lives with minimal limitations. Regular medical check-ups help maintain this quality.
Potential Complications
There are some potential complications. These include infection, shunt malfunction, or other medical issues. It’s important to watch for symptoms like headaches or vision problems. Prompt treatment can manage these complications well.
Living with hydrocephalus requires ongoing care. Still, many people achieve a good balance of health and activity. Support from healthcare professionals and family is key to a positive outcome.
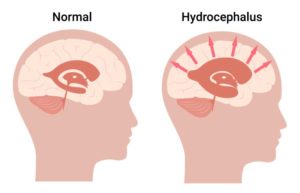
Credit: www.cerebralpalsyguide.com
Research And Advancements
Hydrocephalus, a condition involving fluid buildup in the brain, has prompted significant research. Scientists and medical professionals are continually exploring ways to improve life expectancy and quality of life for those with hydrocephalus. This section delves into recent research and advancements in this field.
New Treatments
Recent advancements have led to new treatments for hydrocephalus. One notable development is the use of programmable shunts. These shunts allow doctors to adjust the fluid flow rate without surgery. This flexibility can significantly enhance patient outcomes.
Another promising treatment is endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV). ETV creates a new pathway for fluid to flow, bypassing obstructions. This procedure can reduce the need for shunts and lower the risk of complications.
Future Directions
Researchers are exploring gene therapy as a potential treatment. By targeting the genetic causes of hydrocephalus, they hope to develop more effective solutions.
Stem cell research also holds promise. Scientists believe that stem cells could repair damaged brain tissue. This could lead to long-lasting improvements in patients’ conditions.
Ongoing clinical trials are testing new drugs. These drugs aim to reduce fluid production in the brain. If successful, they could offer a non-surgical treatment option.
Collaboration between researchers, doctors, and patients is key. Sharing knowledge and experiences can accelerate progress and lead to breakthroughs.

Credit: ana-neurosurgery.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Average Lifespan Of Someone With Hydrocephalus?
The average lifespan of someone with hydrocephalus varies. Many people live a normal lifespan with proper treatment. Early diagnosis and management are crucial.
Can A Person Live A Normal Life With Hydrocephalus?
Yes, many people with hydrocephalus can live normal lives. Early diagnosis and proper treatment are crucial for better outcomes. Regular medical follow-ups help manage the condition effectively.
What Is The Long Term Outlook For Hydrocephalus?
The long-term outlook for hydrocephalus varies. Early diagnosis and treatment improve outcomes. Regular monitoring and proper management are crucial.
Is Hydrocephalus A Terminal Illness?
Hydrocephalus is not always a terminal illness. It can be managed with proper treatment, improving quality of life.
Conclusion
Living with hydrocephalus varies for each person. Medical care plays a big role. Regular check-ups and treatments can help improve life expectancy. Support from family and friends is crucial. Staying informed about the condition helps too. Always consult healthcare professionals for advice.
They know best about managing hydrocephalus. Remember, each case is unique. Understanding and support make a huge difference. Stay positive and proactive.



