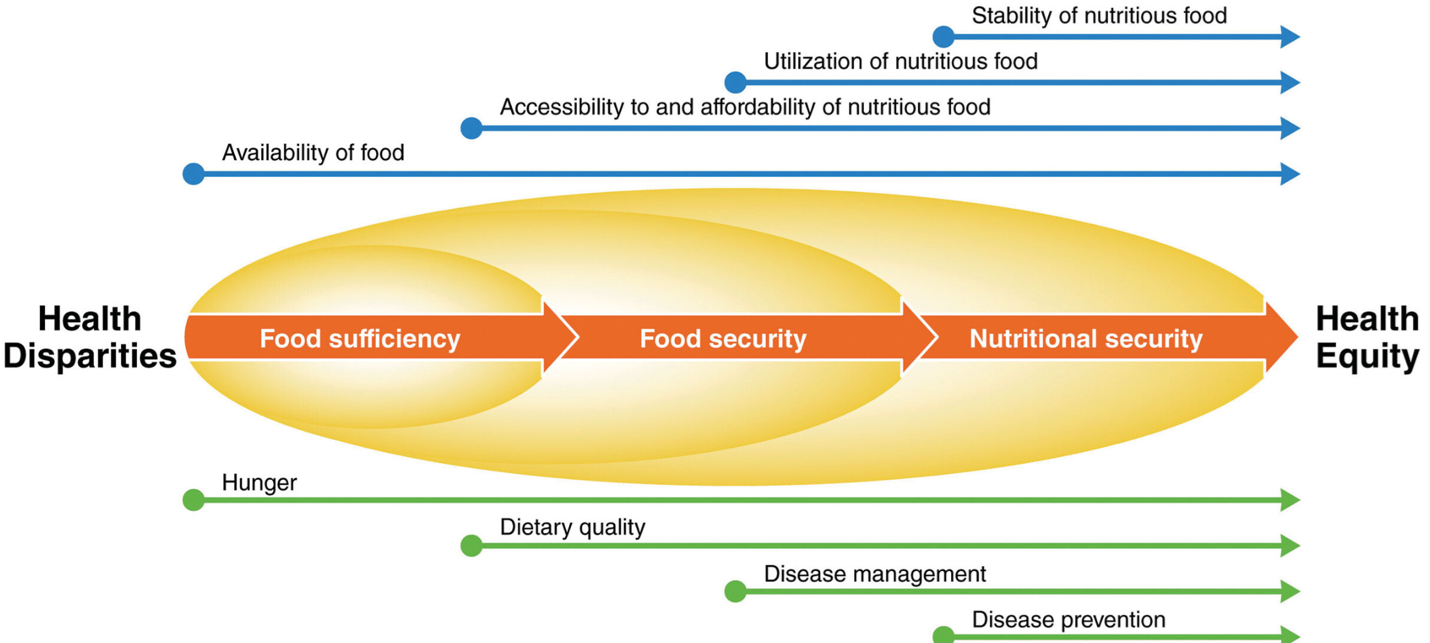
Food security and nutrition security are critical for a healthy life. They seem similar but have distinct meanings.
Understanding the difference helps in addressing global health issues better. Food security means having enough food for all people at all times. It focuses on the availability, access, and stability of food. Nutrition security, however, goes beyond just having food.
It ensures that the food people eat is nutritious and supports a healthy life. This means considering the quality and variety of food, not just the quantity. Knowing these differences is vital for creating effective policies and programs. It helps in promoting better health and reducing malnutrition. Let’s explore these concepts further to understand their unique roles in fostering global well-being.
Defining Food Security
Food security is a term we often hear, but what does it really mean? It’s not just about having enough food. It’s also about making sure the food is available, accessible, and can be properly utilized. Let’s dive deeper into these three important aspects of food security.
Availability Of Food
When we talk about the availability of food, we’re referring to having enough food for everyone. This means there should be a consistent supply of food. Think of it like this: if you go to the market, there should always be food on the shelves. No one should go hungry because there isn’t enough food produced or supplied.
Accessibility To Food
Having food available is one thing, but can everyone get it? Accessibility to food means that people have the means to obtain the food. This can be through purchasing it, growing it, or receiving it as aid. It’s like having a delicious cake in the fridge; it doesn’t help if you can’t open the fridge door or if you can’t afford the cake. Everyone should have fair access to food.
Utilization Of Food
Finally, utilization of food is about how we use the food we have. It’s not just about eating, but about making sure our bodies get the nutrients they need. Proper storage, cooking methods, and knowledge about nutrition play a huge role here. Imagine having a bunch of fresh vegetables but not knowing how to cook them. Or worse, storing them improperly so they spoil. We need to ensure food is used in the best possible way to support health.
Understanding these three components can help us appreciate the full picture of food security. It’s not just about having food; it’s about making sure everyone can get it and use it well.
Defining Nutrition Security
When we talk about nutrition security, we are diving deeper than just having enough food to eat. Nutrition security is about ensuring that everyone has access to the right foods that provide the nutrients needed for a healthy life. It’s not just about filling stomachs; it’s about nourishing the body with what it truly needs.
Adequate Nutrient Intake
Having a plate full of food is good, but is it enough? Not necessarily. Nutrition security ensures that the food consumed has the right nutrients. Think of it like fueling a car; it’s not just about having fuel, but having the right type of fuel. Our bodies need a variety of vitamins and minerals to function properly. For instance:
- Vitamins like A, C, and D
- Minerals such as iron and calcium
- Proteins for muscle repair
- Healthy fats for energy
Ensuring an adequate intake of these nutrients is crucial for growth, development, and maintaining good health.
Balanced Diet
Now, let’s talk about the balanced diet. Picture a well-balanced meal; it’s colorful, varied, and covers all food groups. A balanced diet means eating the right proportions of carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals. Here’s why it matters:
- Carbohydrates provide energy.
- Proteins help in building and repairing tissues.
- Fats are essential for brain health.
- Vitamins and minerals support various bodily functions.
Remember the old saying, “Variety is the spice of life”? It applies perfectly here. A variety of foods ensures you get a mix of nutrients and prevents the monotony of meals.
Health And Well-being
Finally, what’s the end goal of nutrition security? It’s health and well-being. When people have access to nutritious food, they are likely to have better health outcomes. This means fewer illnesses, more energy, and a higher quality of life. Imagine feeling energetic throughout the day because you’ve given your body what it needs. Isn’t that a win?
Moreover, proper nutrition can reduce the risk of chronic diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and obesity. It’s like having a strong foundation for a house; with good nutrition, your body can withstand more and perform better.
In conclusion, while food security ensures that people have enough food, nutrition security ensures they have the right kind of food for a healthy life. It’s about more than just surviving; it’s about thriving.
Key Differences
Understanding the difference between food security and nutrition security is essential. These terms may sound similar but have different meanings. They address various aspects of our food systems. Let’s explore the key differences between them.
Focus On Availability Vs. Nutrient Quality
Food security focuses on the availability of food. It ensures that people have enough food to eat. The main goal is to prevent hunger.
Nutrition security, on the other hand, focuses on the quality of food. It ensures that people get the necessary nutrients. The aim is to prevent malnutrition and promote health.
Short-term Vs. Long-term Impact
Food security often addresses short-term needs. It provides immediate relief to those in need. It aims to solve hunger crises quickly.
Nutrition security focuses on long-term impact. It promotes healthy eating habits over time. It aims to prevent chronic diseases and improve overall well-being.
Measurement Metrics
Food security uses metrics like food availability and access. It measures how much food is available and how easily people can get it. Indicators include food supply and distribution networks.
Nutrition security uses metrics related to nutrient intake. It measures the quality of diets and nutrient deficiencies. Indicators include dietary diversity and micronutrient levels.

Credit: www.researchgate.net
Interrelation Of Food And Nutrition Security
Understanding the difference between food security and nutrition security is crucial for addressing global hunger and malnutrition. But how are these two concepts interrelated? Let’s delve into the interrelation of food and nutrition security, shedding light on their synergistic relationship, the importance of their integration, and the policy implications that arise from this relationship.
Synergistic Relationship
Food security and nutrition security are two sides of the same coin. Food security ensures that people have consistent access to enough food to meet their dietary needs. However, nutrition security goes a step further by ensuring that the food consumed is nutritious and contributes to a healthy life.
Imagine a situation where a community has access to ample food, but the food lacks essential nutrients. While they may not be hungry, they could still suffer from malnutrition due to the poor quality of their diet. On the other hand, if a community has access to nutritious food but not enough of it, they will still face health challenges. Therefore, food security and nutrition security must work hand in hand to ensure overall health and well-being.
Importance Of Integration
Integrating food security and nutrition security is vital for creating sustainable solutions to hunger and malnutrition. By focusing on both quantity and quality, we can address the root causes of health issues and improve overall community health.
Consider a farmer who grows a variety of crops. By ensuring that these crops are both plentiful and nutrient-rich, the farmer can support the health of their family and community. Additionally, integrating education on nutrition can help people make better food choices, leading to long-term improvements in health.
Policy Implications
Policies that address both food security and nutrition security are essential for creating lasting change. Governments and organizations need to develop strategies that ensure access to sufficient, nutritious food for all.
- Investment in agriculture: Supporting sustainable farming practices that produce diverse and nutrient-rich crops.
- Education programs: Teaching communities about the importance of nutrition and how to make healthy food choices.
- Social safety nets: Providing support for vulnerable populations to ensure they have access to nutritious food.
By addressing food security and nutrition security together, policies can create a more comprehensive approach to tackling hunger and malnutrition.
In conclusion, the interrelation of food security and nutrition security highlights the need for a holistic approach to addressing global hunger. By understanding their synergistic relationship, recognizing the importance of integration, and developing effective policies, we can work towards a world where everyone has access to sufficient, nutritious food.
Global Perspectives
Understanding the difference between food security and nutrition security is crucial for addressing global hunger and malnutrition. While food security focuses on the availability and access to food, nutrition security emphasizes the quality of the food and its ability to meet the dietary needs of individuals. Let’s dive into how these concepts are viewed and addressed around the world.
Developed Vs. Developing Countries
In developed countries, the focus is often on ensuring that all citizens have access to a variety of healthy foods. Governments implement policies to support agricultural production, food distribution, and nutrition education. However, issues like food deserts and obesity still persist.
Conversely, in developing countries, the primary challenge is often ensuring there is enough food to go around. Many regions face chronic food shortages due to economic instability, conflict, and climate change. Nutrition security is also a major concern, as the available food may lack essential vitamins and minerals.
Case Studies
Let’s look at some examples to illustrate these differences:
- United States: Programs like SNAP (Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program) aim to provide low-income families with access to nutritious food. Despite these efforts, food insecurity still affects millions.
- India: The Public Distribution System (PDS) is a government-run program that aims to provide subsidized food grains to the poor. Yet, malnutrition remains a significant issue, especially among children.
- Brazil: The Zero Hunger Program was successful in reducing both hunger and malnutrition through a combination of direct food aid, support for local agriculture, and nutrition education.
International Initiatives
Addressing food security and nutrition security requires a global effort. Here are some key initiatives:
- World Food Programme (WFP): Provides emergency food aid and works to improve nutrition in vulnerable communities.
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO): Focuses on increasing agricultural productivity and improving food systems.
- Global Alliance for Improved Nutrition (GAIN): Aims to tackle malnutrition by fortifying foods with essential nutrients and supporting nutrition-sensitive agriculture.
These initiatives highlight the importance of a coordinated approach to ensure everyone has access to safe, nutritious, and sufficient food.
Credit: www.momsmeals.com
Challenges And Barriers
Understanding the difference between food security and nutrition security is essential. Both concepts have unique challenges and barriers. These factors affect efforts to ensure everyone has enough food and proper nutrition.
Economic Factors
Economic factors play a significant role in food and nutrition security. Poverty limits access to nutritious food. High food prices make healthy options unaffordable. Unemployment reduces income, affecting food choices. Economic instability can disrupt food supply chains.
Environmental Issues
Environmental issues impact food and nutrition security. Climate change affects crop yields. Extreme weather damages crops and disrupts food production. Soil degradation reduces agricultural productivity. Water scarcity limits irrigation, affecting food availability.
Social Determinants
Social determinants influence food and nutrition security. Education levels affect dietary choices. Lack of nutrition knowledge leads to poor food choices. Social inequalities impact access to nutritious food. Cultural practices and beliefs shape dietary habits.
Strategies For Improvement
Understanding the difference between food security and nutrition security is crucial. Food security means having enough food. Nutrition security means having the right kind of food to stay healthy. While both are important, improving them needs different approaches. Let’s dive into some effective strategies for improvement.
Policy Changes
Governments play a huge role in ensuring food and nutrition security. Policy changes can make a big difference. Here are some ways to improve:
- Subsidies for Healthy Foods: Lower prices for fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can make them more accessible.
- Support for Local Farmers: Help local farmers grow diverse crops. This ensures a variety of foods is available.
- Nutrition Standards: Set standards for school meals and public institutions. This ensures everyone gets nutritious food.
Community Programs
Local communities can also help improve food and nutrition security. Community programs can be powerful tools. Here are some ideas:
- Community Gardens: These can provide fresh produce to those in need. They also teach people how to grow their own food.
- Food Banks and Pantries: Ensure that these resources provide not just food, but nutritious options.
- Cooking Classes: Teach people how to cook healthy meals with affordable ingredients.
Education And Awareness
Knowledge is power. Educating people about nutrition can lead to healthier choices. Here are some strategies:
- School Programs: Teach children about healthy eating from a young age. This can create lifelong habits.
- Public Campaigns: Use media to spread information about nutrition. Simple tips and easy recipes can encourage better eating habits.
- Workshops and Seminars: Offer these in community centers. They can cover topics like reading nutrition labels and meal planning.
In the end, improving food and nutrition security requires a combined effort. Policy changes, community programs, and education all play a part. By working together, we can ensure everyone has access to the food they need to live healthy lives.

Credit: www.semanticscholar.org
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Difference Between Food Security And Nutrition?
Food security ensures access to sufficient, safe food. Nutrition focuses on the quality of food and its health benefits.
What Is The Difference Between Food Security And Nutrition Security Quizlet?
Food security ensures access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food. Nutrition security focuses on the quality of diet and health outcomes.
What Is Nutrition Security?
Nutrition security ensures consistent access to safe, nutritious food for an active, healthy life. It addresses dietary needs and preferences.
What Is The Difference Between Food And Nutrition?
Food is what we eat for energy and sustenance. Nutrition refers to how food affects our health and body functions.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between food security and nutrition security is crucial. Food security ensures access to enough food. Nutrition security focuses on quality, ensuring a balanced diet. Both are essential for a healthy society. Governments and communities must address both.
Ensuring everyone has access to nutritious food is key. This improves health and well-being. Together, we can achieve a healthier future. Prioritize both food and nutrition security for a better world.